Eco-friendly Production Activities
Environmental management
Environmental vision
The INOAC Group respects the natural environment of our irreplaceable earth and contributes to realizing an affluent society that is comfortable to live in through technology harmonized with our environment and environment-friendly corporate activities.
Environmental policy
- We observe environmental laws and regulations, thoroughly ensure compliance, and engage in business activities that society can trust.
- We work to reduce CO2 emissions such as by saving energy, to help achieve a carbon neutral society and prevent global warming.
- We work on resource conservation, waste reduction and recycling to contribute to a recycling-oriented society.
- We properly manage chemicals that could impact the environment and seek to preserve our environment by reducing risk.
- We actively develop products with less environmental impact, contributing to the conservation of nature throughout the life cycles of the products.
- We engage in environmental management, educate employees about the environment, implement environmental audits, and continue to improve.
- We contribute to establishing a sustainable society through local environmental preservation work as good corporate citizens.
Environmental management system
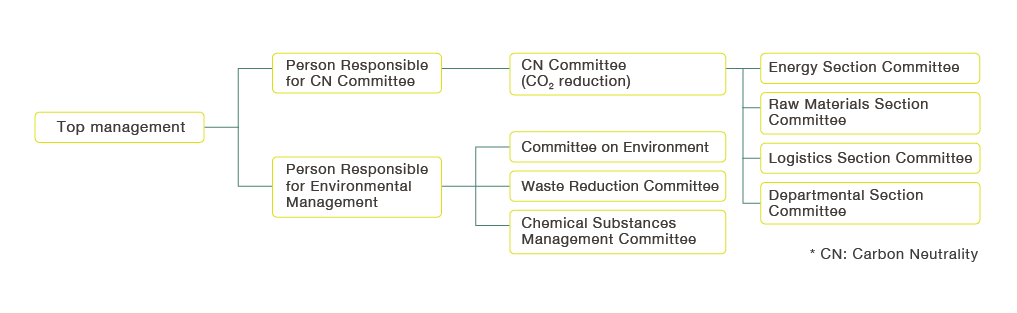
To engage in environmental activities in an organized fashion, we have established our Environmental Preservation Promotion System under the direct control of top management as shown in the figure above. The Person Responsible for CN Committee handles overall management related to reducing CO2 emissions, and we have established four section committees subordinate to the CN Committee. The Person Responsible for Environmental Management handles the overall management of other environmental activities. For that, we have established three committees for environment, waste reduction, and chemical substances respectively. Each committee and section committee engages in activities with clear missions and KPIs. The committees and section committees also coordinate with each other to implement environmental management for INOAC as a whole.
Environmental Preservation Promotion System
Internal environmental audits
We implement internal environmental audits to check the operational state of our environmental management system. The audit team consists of two to three employees who have completed the internal auditor training prescribed by the company. The team checks if the environmental management system is being properly operated, maintained, and improved. We create implementation guidance and revise checklists whenever necessary to emphasize efforts toward goal achievement and legal compliance, among other efforts to audit at a higher level.
External environmental examinations
The Japan Quality Assurance Organization (JQA), an external certification body, conducts examinations to check if our environmental management system is functioning properly in accordance with ISO 14001:2015. In September 2024 we underwent a renewal audit and our renewal was registered without anything being pointed out. Also, as overall findings, some issues were raised in terms of environmental aspects, compliance obligations and evaluations, and processes such as internal audits. We are working to improve what was pointed out as the opportunities arise.
Summary of major activities in FY 2023
Due to factors such as increases in production volume, we were unable to achieve our goal for reducing energy consumption related to CO2 in FY 2023. However, we are continuing our CO2 reduction activities to achieve our goals for FY 2024 and beyond. Steady progress was also made in reducing environmental impact from waste, VOC, PRTR, and water intake. We had zero environmental incidents, including violations of laws and regulations.
| Initiative | Targets in FY 2023 | Achieved in FY 2023 | Targets in FY 2024 | Targets in FY 2030 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing energy consumption (in plants) |
CO2emissions (tons) | 70,637 or less | 73,394 | 68,631 | 45,887 |
| Reducing waste (in plants) | Amount treated (tons) | 10,440 or less | 10,055 | 9,500 | 8,400 |
| Reducing emissions of VOC substances | Amount emitted (tons)/ monetary sum of production (million yen) |
Not specified | 1.82 | 1.81 or less | 1.30 or less |
| Reducing amounts of PRTR substances emitted & transferred | Amount emitted + amount transferred (tons)/ monetary sum of production (million yen) |
2.14 or less | 2.15 | 2.09 or less | Not specified |
| Reducing water intake | Water intake (thousand m3) | 2,319 or less | 2,284 | 2,236 | 2,153 |
| Managing chemical substances | Green procurement rules revisions | Continued new efforts | No revision | Continued new efforts | Continued new efforts |
| Environmental incidents | Major accidents, legal violations,number of complaints | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
* Environment data is collected to summarize major activities from all INOAC Group business locations in Japan.
Reducing our environmental footprint
Addressing climate change (Scope 1 + 2)
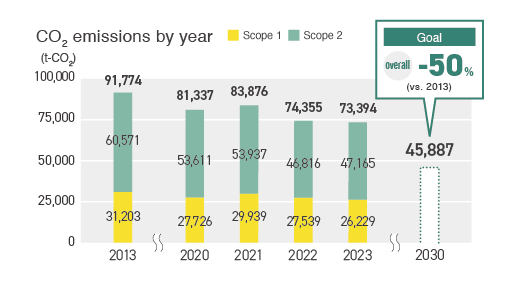
For our management to reduce Scope 1 and 2 emissions in particular, we set the goal of a 50% reduction in 2030 (overall volume in Japan) compared to 2013, and the CN Committee is leading our efforts toward this goal. Specifically, we are assigning CO2 reduction targets for each department and plant, visualizing the items to be reduced, reduction effects, and amounts of related investments, and managing the progress.
Managing chemical substances appropriately
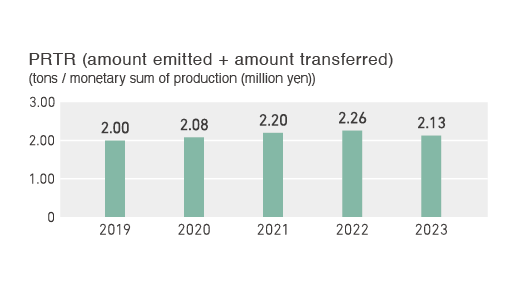
When manufacturing polyurethane foam, we use PRTR substances such as m-tolylene diisocyanate, as well as xylene and toluene which coatings contain. To reduce the amounts of these chemical substances that we handle, release, and transfer, we made progress in reducing dichloromethane which is partially left over as foaming agent, and also in both improving and taking measures against defects in its coating process. Although our emissions + amount transferred of PRTR substances in FY 2023 increased 14% vs. FY 2022, they decreased by 6% vs. FY 2022 in measured units, indicating an improvement trend.
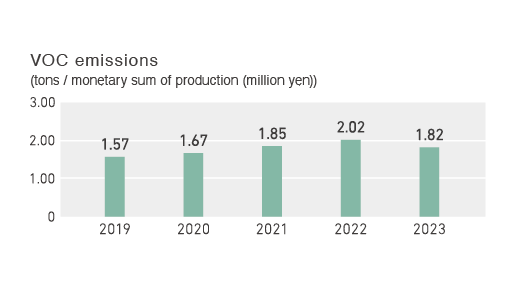
VOCs (volatile organic compounds) emitted into the air react with ultraviolet rays in sunlight, generating photochemical oxidants and airborne particulate matter. Among the raw materials that we use, VOCs contained in materials such as coatings for automotive components and adhesives are released into the air through the action of drying. To reduce VOCs, we strive to mitigate our VOC usage through means such as developing fabrication methods and processes geared toward coating efficiency and spreading dichloromethane-free polyurethane foam technologies as we work to reduce our airborne emissions.
Waste reduction initiatives
Volume of waste (excluding resalable), measured units of sales
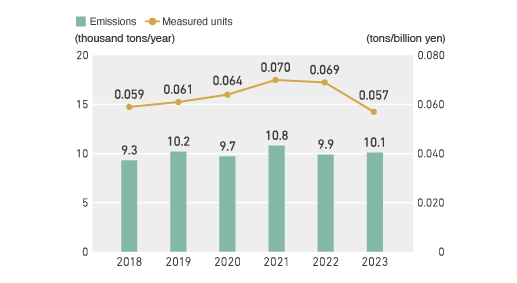
The INOAC Group (domestically) achieved its goal for total volume of waste discharged in FY 2023, but this volume did increase slightly compared to FY 2022. However, through our ongoing activities to reduce defects and improve yield and to recycle rubber and resin materials and convert them into resalable waste, we have been able to reduce emissions in measured units (volume of waste per unit monetary sum of production) by 17%.
Initiatives to reduce water usage
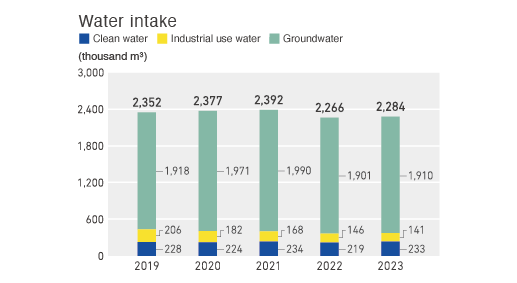
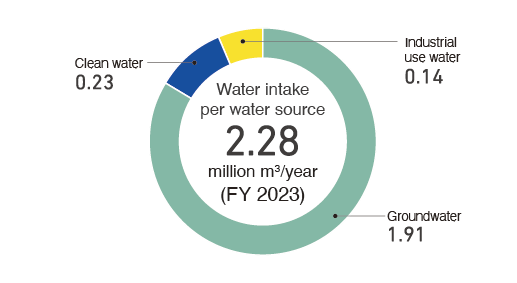
The INOAC Group consumes large volumes of water, including not only water used when manufacturing products but also for cooling molded rubber and plastic products, and the water that our employees drink. We consider water to be a crucial resource. In addition to reducing our water usage through production process improvements and recycling, we will also utilize tools by Aqueduct to address water-related risks. Leveraging these tools, we will pursue the continuity of our business activities by anticipating the risks and conducting interviews in each area to further understand these risks.
Managing information on chemical substances
Observing environmental laws and regulations
The INOAC Group strives to thoroughly observe environmental laws and regulations. In FY 2023 we had zero law violations at locations in Japan and other countries. We will continue striving to have zero environmental incidents. To thoroughly ensure compliance with environmental laws, in Japan the person in charge of environmental efforts at each location participates in Committee on Environment meetings four times per year to touch base about revisions to environmental laws and report on self-directed inspections at each location. Our Quality Division also regularly inspects the observance of ISO14001 EMS at our locations in Japan, verifies the status of their legal compliance, and strives to ensure that violations do not occur..
Major environment-related laws and regulations pertaining to business activities
- Air
- Air Pollution Control Act, Automobile NOx PM Law, Act on Special Measures against Dioxins
- Water quality & soil
- Water Pollution Prevention Act, Purification Tank Act, Sewerage Act, Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act
- Noise, vibration & odor
- Noise Regulation Act, Vibration Regulation Act, Offensive Odor Control Act
- Chemical substances
- Act on Confirmation, etc. of Release Amounts of Specific Chemical Substances in the Environment and Promotion of Improvements to the Management Thereof, Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act
- Resource conservation & recycling
- Act on the Rational Use of Energy, Act on the Promotion of Sorted Collection and Recycling of Containers and Packaging, Act on Rational Use and Appropriate Management of Fluorocarbons, Act on Special Measures concerning Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes, Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act
- Disaster prevention
- Fire Service Act, High Pressure Gas Safety Act
- General & others
- Factory Location Act, Act on Improvement of Pollution Prevention Systems in Specified Factories, Radio Act
* Legal orders such as local government ordinances are omitted * Some of the above are abbreviated
Promoting IMDS, chemSHERPA and more
Information collection through IMDS in INOAC - reporting process and chemical management system
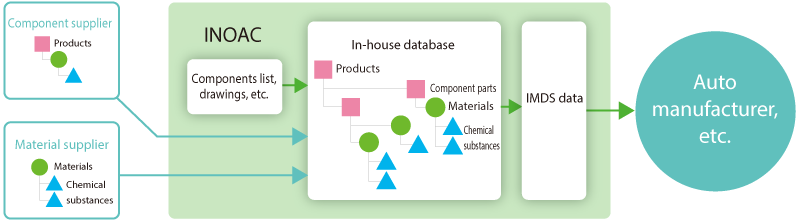
INOAC registers information on chemicals and reports it to our customers through IMDS*1, particularly in the automotive field which is our main field of business. We have a management system to obtain the necessary information via our supply chain and to register the information into IMDS.
- IMDS (International Material Data System): A database for transmitting and obtaining information on materials and chemicals over the internet for the automotive industry, which was originally developed to comply with the EU ELV Directive.。
- chemSHERPA: A unified format to transmit information on chemicals contained in products in the supply chain, which the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry took the initiative in developing.
Creating an in-house database
The Automotive Division is creating an in-house database through which information on chemical substances contained in parts and materials purchased from suppliers is identified based on information about chemical substances, and centrally managed. This has allowed us to be certain of our compliance with laws and regulations on chemical substances and client requirements which increase each year, while also helping to improve the efficiency and the reporting accuracy of information we register in IMDS and when examining the chemical substances contained in our products.
Establishment and implementation of green procurement criteria
We ascertain what chemical substances are regulated by laws, regulations, and by our customers, based on which we create our green procurement criteria - a list of those chemical substances that we should work to reduce. We present these criteria to suppliers and use them to obtain information on chemical substances contained in raw materials to be purchased. We are also consistently monitoring the latest regulatory developments, based on which we revise these criteria once each year.
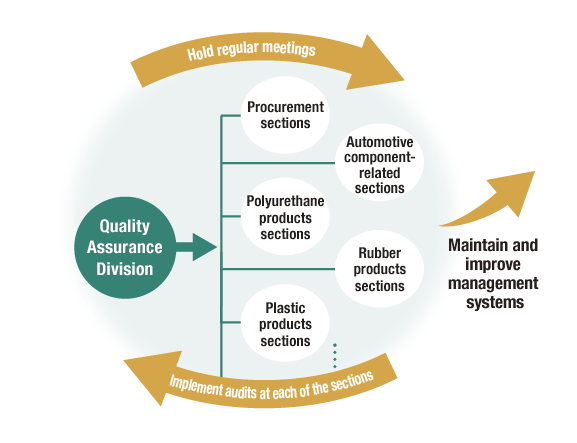
Communication about chemical substance management
The Global Quality Assurance Division is a company-wide organization for environmental stewardship, which takes the lead in organizing internal coordination meetings for chemical substances once every two months, bringing together the sections that manage chemical substances in each department. These meetings are to revise our Green Procurement Standards, observe management systems and establish their operating rules, and exchange opinions concerning the latest trends in chemical regulations such as the REACH regulation* and RoHS Directive*. They also periodically audit the management systems in each department. We strive to maintain and improve chemical substance management systems to ensure that they are appropriate and reliable.
Training for emergencies
We identify accidents and emergencies according to the characteristics of each business facility, and periodically conduct training to prevent and stop the spread of environmental pollution resulting from earthquakes, fires and leakage of oils and raw materials. At the Yana Plant (in Aichi) we hold disaster prevention training evacuation & extinguishing fires) every March and November, and in manufacturing departments we also change scenarios and conduct raw material spill/runoff prevention training every October. In other facilities, training for emergencies and urgent circumstances is conducted on a preparatory basis.





